A Brand of CLT Technologies & Edu-Publishers Pvt. Ltd.
A Brand of CLT Technologies & Edu-Publishers Pvt. Ltd.

Geography is the study of man, his environment and interaction between the two’. This definition of geography tells you about the comprehensive nature of Geography and its vastness. Geography has ‘overlapping’ topics which cover Environment, Economic Geography, Human geography (Demography) and Current Events. One should always have an ATLAS while studying geography. It gives you more insights, makes your reading more meaningful and enjoyable.
While studying Geography, clarity of concepts is needed, which should be substantiated with appropriate facts. Among all the subjects that are included in the syllabus of the Civil services examination, Geography arguably has the largest syllabus. Also, since nearly one-fifth of the paper has questions related to geography and environment, the weightage of the subject is certainly high. The aspirant requires a coherent strategy to be able to cover all the topics. To do this, we have analysed the subject in detail.
ASPIRE IAS MAKES THIS LENGTHY SYLLABUS AND DIFFICULT MAPS EASY FOR YOU WITH QUICK LEARNING IN CLASSROOMS ITSELF. UPSC ORIENTED GEOGRAPHY AND MAPPING CLASSES OF ASPIRE IAS WILL MAKE SURE YOU SCORE FULL MARKS IN GEOGRAPHY.
REMEMBER THAT GEOGRAPHY IDEALLY TAKES NEARLY 3 MONTHS ON YOUR SCHEDULE, THE FIRST TIME AND WITH OUR HELP ONLY LESS THAN A MONTH. PLAN ACCORDINGLY. IF YOU HAVE ANY MORE DOUBTS, FEEL FREE TO REACH OUT TO US IN THE CHAT BOX.
The exam notification says:
Indian and World Geography - Physical, Social and Economic Geography of India and the World.
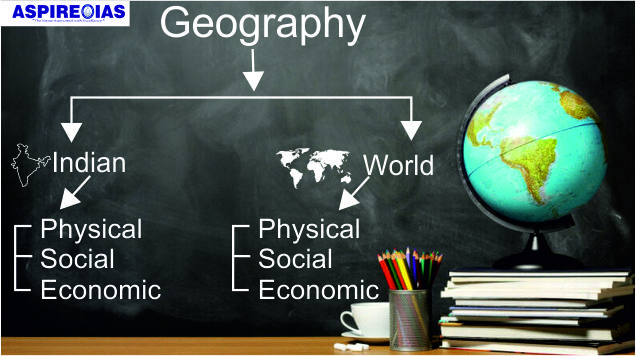
Thus the syllabus has two components:
Your study schedule should ideally have the above divisions. This will allow you to create a checklist to go through so that you can set your targets accordingly
Now, you must learn to sub-categorize the syllabus. A good way is to follow the table of contents given in the NCERTs. The World Geography syllabus is given below:
Since Environment and biodiversity are separate topics in the syllabus parts of Environmental geography and Biogeography are best covered under those sub-headings. This will allow you to cover current affairs in detail as well.
Under World geography, social geography is rarely covered. It is thus advised that you prepare current affairs related topics on:
This covers the syllabus sub-categorisation for world geography. Similarly a breakup of the Indian geography syllabus can be done. A good way is to use the table of contents of the NCERTs which ideally divide the syllabus along logical lines. Here is how we divide the Indian geography syllabus:
Always have an atlas at hand while studying Geography. It is a map-based subject. To be able to understand it you must have a good knowledge of the map. In fact, in the civil services preliminary examination, there were several questions from maps, especially for India.

Our Popular Courses
Module wise Prelims Batches
Mains Batches
Test Series
Copyright 2023 CLT TECHNOLOGIES AND EDU-PUBLISHERS PRIVATE LIMITED. All rights reserved.