Online Learning Portal
Online Learning Portal

The first Union Public Service Commission was set up on October 1st, 1926. However, its limited advisory functions failed to satisfy the people’s aspirations and the continued stress on this aspect by the leaders of our freedom movement resulted in the setting up of the Federal Public Service Commission under the Government of India Act 1935. Under this Act, for the first time, provision was also made for the formation of Public Service Commissions at the provincial level.
The Constituent Assembly, after independence, saw the need for giving a secure and autonomous status to Public Service Commissions both at Federal and Provincial levels for ensuring unbiased recruitment to Civil Services as also for protection of service interests. With the promulgation of the new Constitution for independent India on 26th January, 1950, the Federal Public Service Commission was accorded a constitutional status as an autonomous entity and given the title – Union Public Service Commission. The Union Public Service Commission has been established under Article 315 of the Constitution of India.
The major role played by the Commission is to select persons to man the various Central Civil Services and Posts and the Services common to the Union and States (viz. All-India Services).
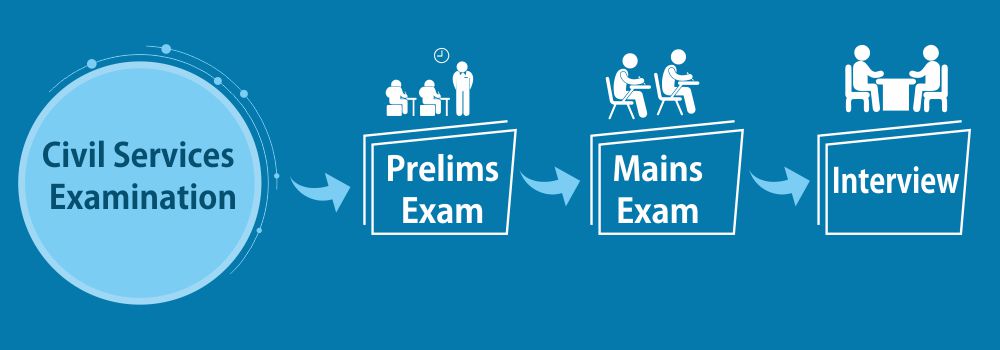
Civil Services Examination is conducted in a cycle of Preliminary exam, Mains Exam and Personality test. All three phases are crucial and the last two phases decide the merit and hence are very significant. Students can attempt the exam after graduation or in the final year of graduation. Every year UPSC notification announces 1000+ vacancies in the top Group A designations.
From the year 2013 the calendar of Civil Service Exam has changed. Earlier mains preparation had nearly 5-6 months but the current pattern gives only 3 months and hence proper planning and good strategy is crucial.
Preparation to Civil Services Examination is a task that demands patience, continued focus and dedicated efforts. The exam is not a test of high intellect or IQ. It is a simple but complete test of basic understanding of issues, personality and orientation in society. With more than 5 lakh students preparing for the exam every year, there are bound to be conceptions, perceptions and beliefs about the exam. These can be both right and wrong!!!
Preliminary Test consists of objective type questions with negative marking scheme for wrong answers. The test is usually held in June.

For a detailed strategy for the Prelims exam, read here.
Qualifying Papers:-
Merit Exams- Candidates will have to score a minimum percentage in the qualifying exam to qualify for the exam. The question papers are prepared to test the intellectual and interpersonal skills of the candidate. The essay type questions will test the students’ understanding of the subject and the concept. The students will be tested on the strength of an Indian Language.
| PAPER | TITLE OF THE PAPER | MARKS ALLOTED |
|---|---|---|
| Paper 1 | Essay Writing | 250 Marks |
| Paper 2 | General Studies – I (Indian Heritage and Culture, History and Geography of the World, and Society) | 250 Marks |
| Paper 3 | General Studies-II (Governance, Constitution, Polity, Social Justice and International Relation) | 250 Marks |
| Paper 4 | General Studies-III (Technology, Economic Development, Bio-Diversity, Environment, Security and Disaster Management) | 250 Marks |
| Paper 5 | General Studies-IV (Ethics, Integrity and Aptitude) | 250 Marks |
| Paper 6 | Optional Subject Paper-1 | 250 Marks |
| Paper 7 | Optional Subject Paper-2 | 250 Marks |
| Sub Total in the written Test | 1750 Marks | |
| Personal Interview | 275 Marks | |
| Grand Total (For Merit Calculation) | 2025 Marks |
For a detailed strategy for the Prelims exam, read here.
The civil services include three types of services namely, the All India Services, Group A and Group B Central services. The services that come under each of these types are mentioned below:
The prescribed UPSC exam eligibility criteria is that the candidate should be a graduate and must have attained 21 years of age. There is also an upper age limit and number of attempts restriction based on the candidate’s category. Generally, the upper age limit is 32 years, but the commission gives age relaxation for OBC, SC, ST and PH candidates.
As we saw above, there are various services candidates can get into after clearing this exam. But the service allotted to the candidate depends on his/her preference indicated while applying for Mains, vacancy in that service for the particular category and the candidate’s rank . Commonly aspired services like the IAS, IFS and the IPS need a high rank.
The UPSC also conducts various other exams apart from the civil services. A few examples are Engineering Services Exam, Combined Medical Services Exam, Indian Forest Service Exam, Combined Defence Services Exam, Indian Statistical Service, etc.
Candidates should know that the civil services and the Indian Forest Services have a common prelims exam. While applying for prelims, candidates should indicate whether they are taking both the exams, or only one of them.
The UPSC Civil Services Exam is tough. This is a fact. But it is also a fact that this exam is not insurmountable. With a systematic approach, hard work and dedication, you can come out with flying colours and land your dream job.
Our Popular Courses
Module wise Prelims Batches
Mains Batches
Test Series
