Online Learning Portal
Online Learning Portal

Monthly DNA
![]() 06 Apr, 2021
06 Apr, 2021
![]() 35 Min Read
35 Min Read
Details of the attack
Maoist insurrection
Conclusion
Source: TH
Implications
Source: TH
Indian astronomers from Aryabhatta Research Institute of Observational Sciences have tracked a rare supernova explosion and traced it to one of the hottest kind of stars called Wolf–Rayet stars or WR stars.
The rare Wolf–Rayet stars are highly luminous objects a thousand times that of the Sun. They strip their outer hydrogen envelope which is associated with the fusion of Helium and other elements in the massive core.
Supernova
Supernovae can be triggered in one of two ways:
Type I supernova or Type Ia supernova
The difference between Nova and Type I supernova
|
Nova |
Type I supernova |
|
In a nova, the system can shine up to a million times brighter than normal. |
A supernova is a violent stellar explosion that can shine as brightly as an entire galaxy of billions of normal stars. |
|
As long as it continues to take gas from its companion star, the white dwarf can produce nova outbursts at regular intervals. |
If enough gas piles up on the surface of the white dwarf, a runaway thermonuclear explosion blasts the star to bits. |
Type II supernova
Importance of supernova: Creating and dispersing new elements
In the supernova explosion, all of these elements are expelled out into space, and new stars are born out of this matter.
Source: PIB
India is fast emerging as a leader in high-power computing with the National Super Computing Mission (NSM) boosting it to meet the increased computational demands of academia, researchers, MSMEs, and startups in areas like oil exploration, flood prediction as well as genomics and drug discovery.
National Supercomputing Mission
The National Supercomputing Mission was launched to enhance the research capacities and capabilities in the country by connecting them to form a Supercomputing grid, with National Knowledge Network (NKN) as the backbone.
The NSM is setting up a grid of supercomputing facilities in academic and research institutions across the country. Part of this is being imported from abroad and part built indigenously.
The Mission is being jointly steered by the Department of Science and Technology (DST) and the Ministry of Electronics and Information Technology (MeitY) and implemented by the Centre for Development of Advanced Computing (C-DAC), Pune, and the Indian Institute of Science (IISc), Bengaluru.
Source: PIB
As 2021 BRICS Chair, India’s approach is focused on strengthening intra-BRICS cooperation based on Continuity, Consolidation and Consensus.
BRICS Finance Ministers and Central Bank Governors discussed the financial cooperation agenda set by India for 2021 - Global Economic Outlook and Response to COVID-19 pandemic, New Development Bank (NDB) Activities, Social Infrastructure Financing and Use of Digital Technologies, Cooperation on Customs related issues, IMF reforms, Fintech for SMEs and Financial Inclusion, BRICS Rapid Information Security channel and BRICS Bond Fund.
BRICS New Development Bank
Source: PIB
Under the Pradhan Mantri Awaas Yojana – Gramin (PMAY-G), 92% target of completion has been achieved in the 1st phase of the scheme i.e. from 2016-17 to 2018-19 with intended beneficiaries also coming down from 2.95 cr to 2.14 cr due to duplication and other incidences.
Rural Housing In India
Pradhan Mantri Awas Yojana- Gramin
Source: PIB
Global Gender Gap Report 2021 was released recently.
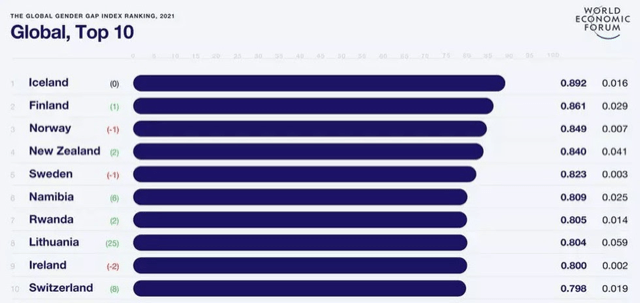
Key takeaways
World Economic Forum (WEF):
WEF Davos Agenda Summit,2021:
The Great Reset Initiative of World Economic Forum-
Source: WEF
Recently Min of Food Supplies talked about modernizing Central Warehousing Corporation and improving its storage capacities.
Other modernizing aspects that were talked about were:
Central Warehousing Corporation
Source: PIB
US Visa regime during the Biden era Introduction Biden shows intent on reworking immigration rules by not extending the H-1B visa ban Details President Joe Biden allowed a ban on the issuance of H-1B visas for skilled workers to lapse at the end of March 2021.. Mr. Biden&rsquo
National Policy for Rare Diseases, 2021- Analysis Introduction The recent notification of the National Policy for Rare Diseases 2021 is pegged on this principle of inclusion. Details of the policy It offers financial support for one-time treatment of up to ?20 lakh, Introduce
Blockchain Enabled Interface for Indian Spices Spices Board India and UNDP India's Accelerator Lab sign MoU to develop a blockchain-powered traceability Interface for Indian spices. This new interface will serve to enhance transparency in the supply chain and trade. India is the
Impacts of Desert Dust Particles on Indian Summer Monsoon A new study shows the impacts of desert dust coming from the West, Central, and East Asia in the Indian Summer Monsoon. Impact of Desert Dust Particles on Indian Summer Monsoon: Strong winds carry the dust particles from the
Exercise La Perouse Indian Navy Ships are participating, for the first time; in the multi-lateral maritime exercise La Pérouse, conducted in the Eastern Indian Ocean Region The Indian Navy ships and aircraft will exercise with ships and aircraft of the French Navy, Royal Au
Advanced Chaff Technology by DRDO for Naval Safety DRDO has developed an Advanced Chaff Technology to safeguard the naval ships against enemy missile attacks. The successful development of Advanced Chaff Technology by DLJ is another step towards Atmanirbhar Bharat. Ch
Increased FDI Inflows in FY 2020-21 India has attracted the highest ever total FDI inflow of US$ 81.72 billion during the financial year 2020-21 and it is 10% higher as compared to the last financial year 2019-20 (US$ 74.39 billion). FDI equity inflow grew by 19% in the F.Y. 2020-21 (US$ 59
Phase III eCourts Project of Supreme Court In another major initiative, the eCommittee Supreme Court has prepared the draft vision document for Phase III of the eCourts Project under the auspices of the Supreme court of India. E-Courts Project is a mission mode project undertaken by t
Stand Up India Scheme Stand up India Scheme was launched on 5th April 2016 to promote entrepreneurship at grassroots level focusing on economic empowerment and job creation. This scheme has been extended up to the year 2025. The objective of Stand-Up India is to promote entrepreneurship amon
Integrated Health Information Platform (IHIP) The Integrated Health Information Platform is the next generation highly refined version of the presently used Integrated Disease Surveillance Programme (IDSP). We have started a new chapter in India’s public health trajectory. India
PLI Scheme for White Goods Taking another important step towards the vision of 'Atmanirbhar Bharat', the Union Cabinet, chaired by the Prime Minister, Shri Narendra Modi, approved the Production Linked Incentive (PLI) Scheme for White Goods (Air Conditioners and LED Lights) with a budg
PLI scheme: 'National Programme on High-Efficiency Solar PV Modules The Cabinet has approved the Ministry of New & Renewable Energy's proposal for the implementation of the Production Linked Incentive (PLI) Scheme 'National Programme on High-Efficiency Solar PV (Photo Volt
How Asian desert dust enhances Indian summer monsoon Dust swarms can influence moisture transport, increase precipitation, rainfall Carl Sagan once described Earth as a ‘small speck of dust, a seemingly insignificant tiny particle. But the dust has incredible power: it is known to i
Indian Army to participate in Exercise “Shantir Ogroshena-2021” About Exercise ‘Shantir Ogroshena-2021’: Exercise Shantir Ogroshena (Front Runner of the Peace) is a multinational military exercise. The 2021 edition of the Exercise will be held in Bangladesh. It
India contributes $300,000 to UN Women India recently announced the contribution of USD 300,000 to the UN Women to support gender equality and women empowerment. About UN Women: UN Women is the United Nations entity, dedicated to promoting gender equality and the empowerment of wom
National Policy for Rare Diseases 2021 Released The Union Health Ministry recently released the policy. Rare Diseases: WHO defines a rare disease as a lifelong disease or disorder that often highly weakens an individual. It has a prevalence of 1 or less per 1000 population. Example: Hae
NITI Aayog's “AIM-PRIME” scheme to support science-based startups Atal Innovation Mission (AIM), NITI Aayog with Bill & Melinda Gates Foundation launched AIM-PRIME (Program for Researchers on Innovations, Market-Readiness & Entrepreneurship). About AIM-PRIME: AIM-
Our Popular Courses
Module wise Prelims Batches
Mains Batches
Test Series